BI-RADS Classification: Reference Guide



The guide below is intended as a quick reference for mammography technologists. Whether you are studying to take your boards, or whether you simply need a refresher for presenting cases to the radiologist in your radiology department, or if you are simply curious and interested in learning more, the guide below will provide you with a clear and concise overview of the BI-RADS classification system for mammograms.
BI-RADS is an acronym for Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System. Proposed by the American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS was implemented in order to standardize the reporting of mammograms and make them more comprehensible to other radiologists and non-radiologists. BI-RADS is now a widely accepted risk assessment, reporting, and quality assurance tool in mammography, MRI, and ultrasound.
There are 7 BI-RADS categories. Click on the toggle for each BI-RADS classification below for more information about that classification.
BI-RAD 0
Category 0 denotes an incomplete evaluation due to insufficient information. In this case, further imaging or information is required. For example, if a screening mammogram shows a round nodule and the radiologist suspects it might be a cyst (not cancer), the radiologist may ask for an MRI or ultrasound and assign a BI-RAD 0 category to the mammogram.
BI-RAD 1
A category 1 classification indicates a normal mammogram with a negative test result. The breasts are symmetrical, and there is no opacity, architectural distortion, or suspected calcification.
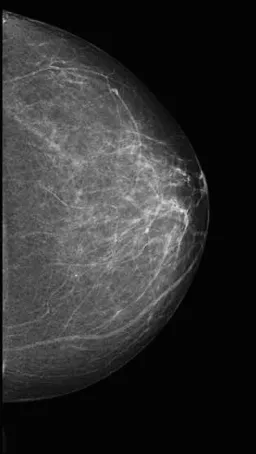
BI-RAD 2
Category 2 indicates an anomaly known to be benign was found in the breast, with 0% probability of malignancy.
- Round opacities with micro-calcifications
- Intra-mammary lymph nodes
- Images of fatty or mixed density
- Known scars
- Isolated macro-calcifications
- Sedimentary micro-calcifications
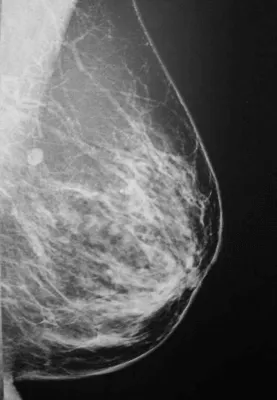
BI-RAD 3
Category 3 means the finding is probably a benign anomaly (i.e., there is a greater than 98% probability of the anomaly being benign).
- Round or oval, discreetly polycyclic non-calcified and well-confined opacities
- Density focal asymmetries with a concave contour and/or mixed with fat
- Round, regular micro-calcifications with unique or multiple focal points, or dispersed without particular clustering
- 6 months for the micro-calcifications, then annual screening. Spot imaging or magnifications
- 4 months for the opacities, then annual screening. Spot imaging or magnifications and/or ultrasound
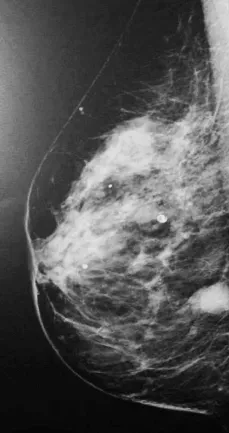
BI-RAD 4
A category 4 classification means the mammogram shows a suspicious abnormality with a 2% to 94% probability of malignancy.
Abnormalities in this classification are lesions that do not have all the morphological characteristics of a typical cancer, but have a significant probability of being malignant. Thus, a histological verification is necessary.
- The punctiform, regular, multiple, and/or clustered micro-calcifications
- The amorphous, grouped, and numerous micro-calcifications
- The irregular, polymorphous, or granular and few micro-calcifications
- BI-RAD 4A: low malignancy suspicion (2-9%)
- BI-RAD 4B: moderate malignancy suspicion (10-49%)
- BI-RAD 4C: high malignancy suspicion (50-94%)

BI-RAD 5
Category 5 indicates that the mammogram shows there are highly suspicious anomalies with a greater than 95% probability of malignancy.
- Opacities with blurry or ill-defined borders
- Opacities with speculated borders
- Granular micro-calcifications, often polymorphic
- Linear and vermicular micro-calcifications
- Evolutionary or micro-calcifications associated with an architectural rupture or an opacity
A guided biopsy is useful to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the proposed treatment includes the sentinel node technique or neo-adjuvant chemotherapy.

BI-RAD 6
A category 6 classification indicates that the previous results of a known biopsy are proved malignant. This category is used in the extension and pre-therapeutic assessment of the biopsied malignant lesions. Appropriate action must be taken.